Mast Cell Activation Disorder (MCAS)
““The severity of MCAS often permanently ‘steps up’ to a higher baseline level following severe stress.”
― Lawrence B. Afrin“Many MCAS patients have been so ill for so long that they have come to accept various aspects of their illness as a baseline “healthy” (or at least “normal”) state for them.”
― Lawrence B. AfrinWhen patients consult their primary care doctor with many seemingly random dramatic complaints affecting unrelated organ symptoms, which often feature prominent psychiatric symptoms, they are often thought to be suffering from a psychosomatic condition and told "its all in your head.” They may be sent home with a prescription for an antidepressant or anti-anxiety medicaiton, which not only is experienced as invalidating but does not address the root cause of their symptoms.
― Judy S Tsafrir M.D.Mast Cell Activation Syndrome (MCAS): When the Body is on Fire
"It feels like being allergic to life."
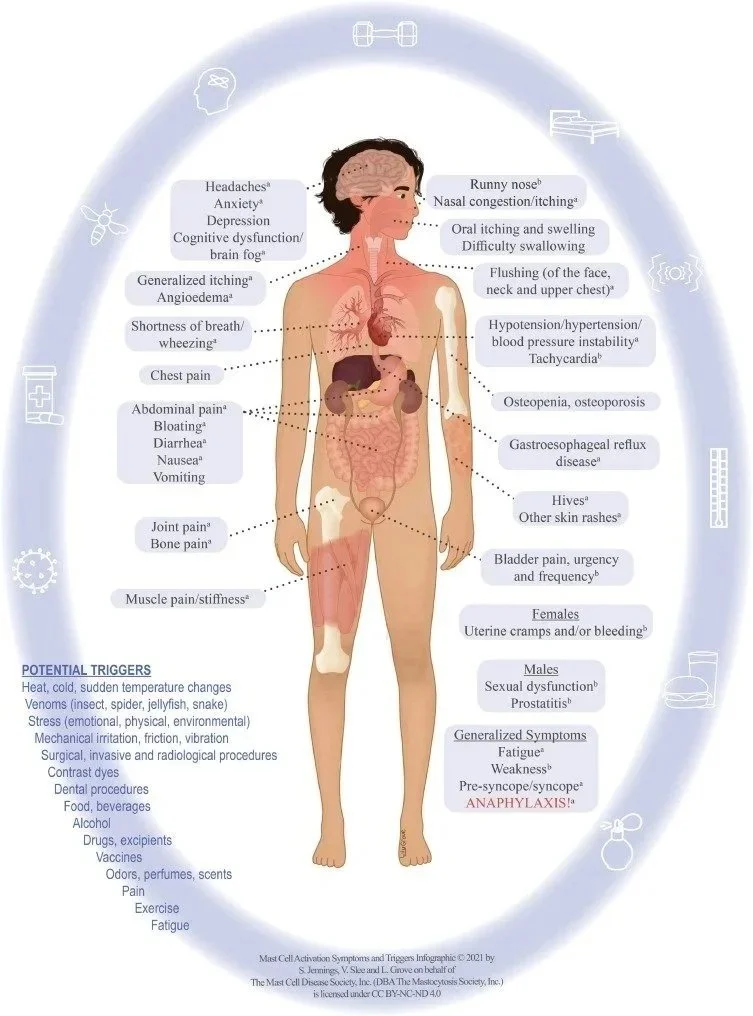
Mast Cell Activation Syndrome (MCAS) is not just "allergies." It is a systemic immune dysfunction where the body's defense system goes rogue. Your mast cells—which are supposed to protect you from invaders—start reacting to everything as a threat: Food, stress, heat, smells, even your own hormones.
The Result: A chaotic storm of symptoms that migrate and shift. One day it’s hives. The next day it’s panic attacks. The next day it’s crushing fatigue. Because the symptoms are so random, patients are often told they are "hypochondriacs" or "anxious." You are not anxious. You are inflamed.
The "Neuro-Psychiatric" Mimic
This is where my work as a therapist is vital. MCAS is a Great Mimic. Because mast cells release histamine and other inflammatory chemicals directly into the brain (Neuroinflammation), MCAS often looks like:
Treatment-Resistant Depression
Sudden-Onset Anxiety or Panic
"Bipolar" Mood Swings (that track with flare-ups, not cycles)
Brain Fog & Memory Loss
If you have been in therapy for years and "talk therapy" hasn't touched your anxiety, we need to ask: Is this a thought, or is this a chemical reaction? I help you distinguish between Psychological Distress and Biological Inflammation. When we treat the mast cells, the "mental illness" often evaporates.
The Causes: Why is this happening?
It isn't just bad luck. It is often a Perfect Storm of:
Genetics (RCCX): The link to Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (EDS). If your tissue is loose, your mast cells are twitchy.
Trauma: Chronic stress primes the mast cells to be hyper-vigilant.
Environment: Mold, viral triggers (like Mono/EBV or Covid), and toxins.
My Approach: Stabilization & Strategy
Living with MCAS is a full-time job. It requires vigilance, planning, and grief processing. I am not a doctor, but I act as a strategist for your care.
1. The Medical Strategy I help you track your triggers (Dietary, Environmental, Stress) so you can bring clean data to your Immunologist. We talk about the role of H1/H2 blockers, Mast Cell Stabilizers, and Low Histamine Diets—not as "rules," but as experiments to find your baseline.
2. The Nervous System Regulation Mast cells are listening to your Vagus Nerve. If you are in "Fight or Flight," they degranulate. We use Somatic Experiencing and Vagus Nerve Stimulation to send a "Safety Signal" to your immune system. Calm the mind, calm the cell.
3. The Food Trauma MCAS creates a terrifying relationship with food. Eating becomes Russian Roulette. We work to heal the Food Fear while respecting the Biological Limits. I help you navigate the grief of a restricted diet while finding joy and nourishment again.
You are not imagining this. The fire in your body is real. But we can turn down the heat.